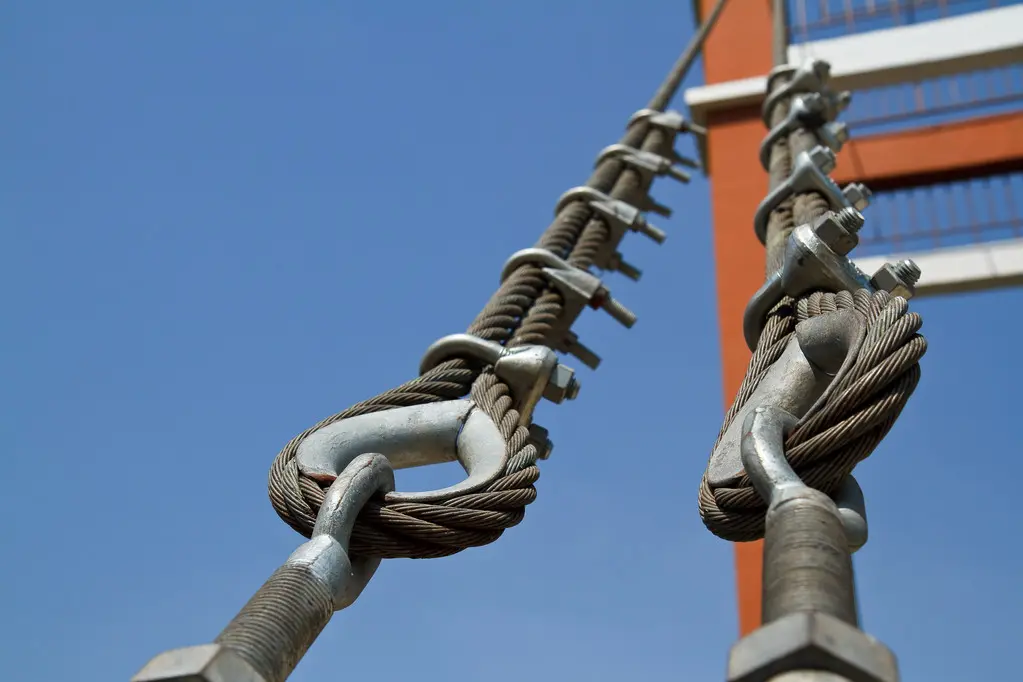
Causes of bending fatigue of hot-dip galvanized steel wire rope
Bending fatigue of hot-dip Galvanized Steel Wire Rope is caused by it running overhead or opening and closing on a single-layer drum.
Fatigue cracks usually initiate at the point of contact between the outer wire and the sky or drum surface or at the intersection between
individual steels. Then the cracks continue to increase with the number of bends, causing fractures perpendicular to the axial direction of
the steel wire. Fatigue wire breakage occurs more often on the inside of a wire rope bend (at the point of contact with the sky) than on
the outside of the bend (at the point of highest bending stress). The fatigue resistance of hot-dip galvanized steel wire ropes generally
increases as the number of outer wires of the rope increases and the diameter decreases.
The durability of a wire rope can also be increased by increasing the diameter of the drum or by reducing the rope tension. Wear or corrosion
may increase the rate of crack formation and crack propagation. However, good wire rope lubrication and re-lubrication during use will reduce
friction between rope elements and thereby improve the fatigue resistance of hot-dip galvanized wire ropes.
Bending fatigue breaks in wire ropes made from compacted outer strands. The distribution of bending fatigue broken wires is usually random. Wire rope bending fatigue wire breakage
A severely worn wire rope with some fatigue broken wires. Due to the twisting of the wire rope, the ends of the broken wires are displaced in different directions.
This 6-strand wire rope showed almost no wear and tear, but a large number of fatigue broken wires.