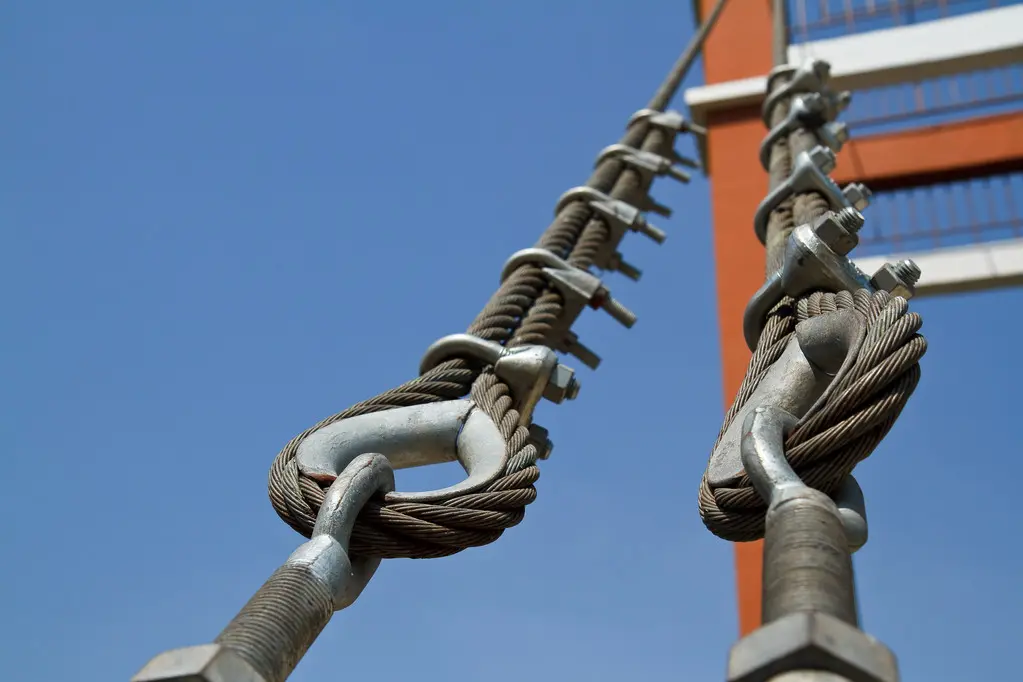
How is galvanized steel wire rope formed
Galvanized Steel Wire Ropes are divided into two categories: cold-dip galvanized steel wire ropes and hot-dip galvanized steel wire ropes. The essential difference between hot-dip galvanizing and cold-dip galvanizing is that the physical heat diffusion of hot-dip galvanizing is to form an active coating. First, an iron-zinc compound is formed, and then a pure zinc layer is formed on the surface of the iron-zinc compound. Electro-galvanizing of galvanized steel wire ropes uses an external power source to obtain an improved coating through electrodeposition. The resulting coating is composed of fine pure zinc particles. The specific content is divided into products: What is the technical difference between hot-selling zinc steel wire rope and cold-dip galvanized steel wire rope?Cold galvanizing is galvanizing at room temperature using electroplating or other methods. In theory, any early zinc coating can be obtained by galvanizing. The zinc content of the galvanized layer can now reach 1200g//u002Fm2, and the general zinc content of the galvanized layer can reach 750g//u002Fm2. Hot-dip galvanizing relies on the physical thermal diffusion coefficient to form different coatings. First, we form an iron-zinc compound, and then react on the surface of the iron-zinc compound to form a pure zinc layer. The highest zinc volume on hot-dip galvanizing is 593a/m2. Hot-dip galvanizing will reduce the mechanical properties of the steel wire, placing higher requirements on high-strength, corrosion-resistant galvanized steel wire ropes. Galvanized steel is a commonly used twisted wire. Hot-dip galvanizing is performed in molten zinc at 450-480 degrees.